Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
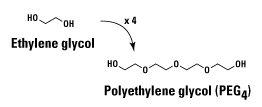
Polyethylene glycol is a biologically inert, non-immunogenic chemical that confers greater water solubility to proteins, labeling tags and crosslinkers with which it is incorporated as constituent chemical group. This page provides a brief introduction to the use and types of PEG reagents available to protein biology researchers.
What is polyethylene glycol (PEG)?
PEG is the common abbreviation for polyethylene glycol – or, more properly, poly(ethylene glycol) – which refers to a chemical compound composed of repeating ethylene glycol units.
Poly ethylene glycol (PEG) is such kind of polymer, with nontoxic, nonimmunogenic, nonantigenic properties, and has been approved by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for drug delivery. To date, PEGylated proteins, peptide, antibody fragments, and oligonucleotides have been approved to execute clinical trials. PEGylated prodrugs were mainly designed to improve the pharmaceutical properties of their parent forms (solubility, stability or permeability) with simple structural modification (mainly conjugation).
Synthesis of PEG
Depending on how one chooses to define the constituent monomer or parent molecule (as ethylene glycol, ethylene oxide or oxyethylene), PEG compounds are also known as PEO (polyethylene oxide) and POE (polyoxyethylene):
Purified PEG is most commonly available commercially as mixtures of different oligomer sizes in broadly or narrowly defined molecular weight (MW) ranges. For example, "PEG 600" typically denotes a preparation that includes a mixture of oligomers having an average MW of 600. Likewise, "PEG 10000" denotes a mixture of PEG molecules (n = 195 to 265) having an average MW of 10,000g/mol.
Properties of PEG
Poly (ethylene glycol) has several chemical properties that make it especially useful in various biological, chemical and pharmaceutical settings:
Non-toxic and non-immunogenic – can be added to media and attached to surfaces and conjugated to molecules without interfering with cellular functions or target immunogenicities
Hydrophilic (aqueous-soluble) – attachment to proteins and other biomolecules decreases aggregation and increases solubility
Highly flexible – provides for surface treatment or bioconjugation without steric hindrance
Defined-length PEG reagents
Precise and versatile application of PEG in proteomics and other biological research methods depends upon the availability of polyethylene glycol derivatives of defined length (MW) that are activated with specific functional groups. Thermo Scientific Pierce Protein Research Products include a diverse array of such PEG-containing reagents. These Pierce Products provide the building blocks required to covalently attach or modify surfaces, proteins and other molecules with PEG-containing derivatives, a process called PEGylation. By contrast with traditional PEG compounds, Pierce PEGylation Reagents are composed of precisely-defined numbers of PEG units. The remainder of this page describes the various classes of Pierce PEGylation Reagents.
Crosslinkers with PEG spacers
Many kinds of Pierce Crosslinkers are available for protein, peptide and other macromolecular immobilization and conjugation needs. Both homobifunctional (identical reactive groups at either end) and heterobifunctional (different reactive groups at either end) crosslinkers are offered with a variety of spacer-arm lengths, solubility and cleaving characteristics.
The wide selection of crosslinking reagents now includes those that contain discrete-length polyethylene glycol spacers. These PEG groups increase reagent and conjugate solubility, minimize toxic and immunological effects compared to non-PEG spacers, and provide several options for accommodating specific crosslinking distances.
Amine-reactive pegylated crosslinkers
The BS (PEG) n reagents are homobifunctional, amine-to-amine crosslinkers that contain N-hydroxy-succinimide (NHS) esters at both ends of a PEG spacer spacer.
An amine-reactive crosslinker that contains a PEG spacer arm. Thermo Scientific Pierce BS (PEG) 5 is a bis-succinimide ester-activated PEG compound used for crosslinking between primary amines (—NH2) in proteins and other molecules. The N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (NHS) groups at either end of the PEG5 spacer react specifically and efficiently with lysine and N-terminal amino groups at pH 7-9 to form stable amide bonds.
Sulfhydryl-reactive pegylated crosslinkers
BM (PEG) n reagents are homobifunctional, sulfhydryl-reactive crosslinkers that contain the maleimide group at either end of a PEG spacer.
A sulfhydryl-reactive crosslinker that contains a PEG spacer arm. Thermo Scientific Pierce BM (PEG) 3 is a bismaleimide-activated PEG compound for crosslinking between sulfhydryl (—SH) groups in proteins and other thiol molecules. The maleimide groups at either end of the PEG3 spacer react specifically and efficiently with reduced sulfhydryls at pH 6.5-7.5 to form stable thioether bonds.
Bifunctional pegylated crosslinkers
The SM (PEG) n reagents are amine-to-sulfhydryl linkers that contain an NHS ester at one end and a maleimide group at the other. SM (PEG) n crosslinkers have the same heterobifunctional structure as the popular reagent SMCC (Part No. 22360 or 22322). Six varieties with 2 to 24 PEG units provide spacer lengths from 18 to 95 angstroms.
Amine-to-sulfhydryl crosslinkers that contain a PEG spacer arm. Thermo Scientific Pierce SM (PEG) n is a series of amine-to-sulfhydryl crosslinkers that differ in length from 17.6 to 95.2 angstroms as a result of polyethylene glycol spacer arms containing n equals 2 to 24 ethylene glycol units.
PEG-containing biotinylation reagents
Labeling antibodies and other molecules with biotin is the basis for many assay and purification platforms used in all areas of proteomics and molecular biology research. Thermo Scientific Pierce EZ-Link Biotinylation Reagents have many different target reactivities, spacer arm lengths, and solubility and cleavability characteristics.
Amine-reactive pegylated biotinylation reagents
The wide selection of biotin-labeling reagents now include several classes of compounds that incorporate discrete-length polyethylene glycol groups as the primary constituent of the spacer arm. These PEG groups increase reagent and conjugate solubility and minimize toxic and immunological effects compared to non-PEG spacers. The alternative spacer lengths enable optimization of conjugate function for specific biotin-binding assays involving streptavidin, avidin or NeutrAvidin Protein.
NHS-PEG4-Biotin is the PEG equivalent of the popular Sulfo-NHS-LC-Biotin (Part No. 21335) and related reagents. Although the PEG analogs do not use the water-soluble Sulfo-NHS form of the amine-reactive group, equivalent reagent water solubility and membrane impermeability are conferred by the hydrophilic polyethylene glycol spacer arm. In addition, experiments have demonstrated that antibodies labeled with PEG-containing biotin tags retain better solubility (less aggregation during long-term storage) than those labeled using non-PEG counterparts.
NHS-PEG4-Biotin is an example of an amine-reactive biotinylation reagent with a PEG spacer arm. Thermo Scientific EZ-Link NHS-PEG4-Biotin is a pegylated, water-soluble reagent for simple and efficient biotin labeling of antibodies, proteins and other primary amine-containing macromolecules.
Sulfhydryl-reactive Pegylated Biotinylation Reagents
Maleimide-PEG11-Biotin is an example of a sulfhydryl-reactive biotinylation reagent with a PEG spacer arm. Thermo Scientific EZ-Link Maleimide-PEG11-Biotin is a long, maleimide-activated, sulfhydryl-reactive biotinylation reagent that includes an 11-unit polyethylene glycol spacer arm for increased water-solubility and reach.
Other pegylated biotinylation reagents
Hydrazide-PEG4-Biotin product is a carbohydrate-reactive biotinylation reagent with a PEG spacer arm. Thermo Scientific EZ-Link Hydrazide-PEG4-Biotin (also called Biotin-PEG4-Hydrazide) is an aldehyde-reactive biotinylation reagent that contains a 4-unit polyethylene glycol (PEG) spacer arm for increased hydrophilicity.
PEG CATALOG
We offer these PEG products in scale from gram to multi-kilo. Industrial quantity products will be produced in state-of-the-art facility in Dalian province. We are glad to accept big pharma and other clients' inspection.
| Catalog No. | Product Name | Cas | M.F. | M.W. | |
| 300006 | PropargylPEG6-CH2CH2COOH | 1951438-84-8 | C16H28O8 | 348.4 | |
| 300007 | PropargylPEG8-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C20H36O10 | 436.5 | |
| 300008 | PropargylPEG10-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C24H44O12 | 524.59 | |
| 300009 | PropargylPEG13-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C30H56O15 | 656.76 | |
| 300010 | PropargylPEG14-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C32H60O16 | 700.81 | |
| 300020 | PropargylPEG5-NH2 | 1589522-46-2 | C13H25NO5 | 275.34 | |
| 300021 | PropargylPEG6-NH2 | 1198080-04-4 | C15H29NO6 | 319.4 | |
| 300022 | PropargylPEG8-NH2 | 1196732-52-1 | C19H37NO8 | 407.5 | |
| 300040 | PropargylPEG5-tBu ester | 1245823-50-0 | C18H32O7 | 360.44 | |
| 300041 | PropargylPEG6-tBu ester | 1355197-95-3 | C20H36O8 | 404.5 | |
| 300042 | PropargylPEG7-tBu ester | 1818294-29-9 | C22H40O9 | 448.55 | |
| 300043 | PropargylPEG8-tBu ester | N/A | C24H44O10 | 492.6 | |
| 300044 | PropargylPEG10-tBu ester | N/A | C28H52O12 | 580.71 | |
| 300045 | PropargylPEG14-tBu ester | N/A | C36H68O16 | 756.92 | |
| 300071 | Amino-PEG3-Amine | 929-75-9 | C8H20N2O3 | 192.3 | |
| 300072 | Amino-PEG4-Amine | 68960-97-4 | C10H24N2O4 | 236.3 | |
| 300073 | Amino-PEG5-Amine | 72236-26-1 | C12H28N2O5 | 280.36 | |
| 300074 | Amino-PEG7-Amine | 332941-25-0 | C16H36N2O7 | 368.5 | |
| 300075 | Amino-PEG8-Amine | 82209-36-7 | C18H40N2O8 | 412.5 | |
| 300076 | Amino-PEG9-Amine | 474082-35-4 | C20H44N2O9 | 456.6 | |
| 300077 | Amino-PEG10-Amine | 928292-69-7 | C22H48N2O10 | 500.6 | |
| 300078 | Amino-PEG11-Amine | 479200-82-3 | C24H52N2O11 | 544.7 | |
| 300079 | Azido-PEG1-Amine | 464190-91-8 | C4H10N4O | 130.1 | |
| 300080 | Azido-PEG2-Amine | 166388-57-4 | C6H14N4O2 | 174.2 | |
| 300081 | Azido-PEG3-amine | 134179-38-7 | C8H18N4O3 | 218.3 | |
| 300082 | Azido-PEG4-Amine | 951671-92-4 | C10H22N4O4 | 262.3 | |
| 300083 | NH2-PEG6-NH2 | 516493-93-9 | C12H26N4O5 | 306.4 | |
| 300084 | NH2-PEG7-NH2 | 957486-82-7 | C14H30N4O6 | 350.4 | |
| 300085 | NH2-PEG8-NH2 | 1333154-77-0 | C16H34N4O7 | 394.5 | |
| 300086 | Azido-PEG8-amine | 857891-82-8 | C18H38N4O8 | 438.5 | |
| 300087 | Azido-PEG10-amine | 912849-73-1 | C22H46N4O10 | 526.6 | |
| 300088 | NH2-PEG12-NH2 | 1800414-71-4 | C24H50N4O11 | 570.7 | |
| 300089 | NH2-PEG24-NH2 | 749244-38-0 | C48H98N4O23 | 1099.3 | |
| 300090 | NH2-PEG36-NH2 | N/A | C72H146N4O35 | 1627.9 | |
| 300097 | NH2-PEG5-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1446282-18-3 | C17H35NO7 | 365.5 | |
| 300098 | NH2-PEG6-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1286281-32-0 | C19H39NO8 | 409.5 | |
| 300099 | NH2-PEG8-CH2CH2COOtBu | 756526-06-4 | C23H47NO10 | 497.6 | |
| 300100 | NH2-PEG9-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1818294-44-8 | C25H51NO11 | 541.7 | |
| 300101 | NH2-PEG10-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1818294-42-6 | C27H55NO12 | 585.7 | |
| 300102 | NH2-PEG12-CH2CH2COOtBu | 872340-65-3 | C31H63NO14 | 673.8 | |
| 300103 | NH2-PEG24-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1104076-62-1 | C55H111NO26 | 1202.5 | |
| 300104 | NH2-PEG36-CH2CH2COOtBu | 872340-65-3 | C79H159NO38 | 1731.1 | |
| 300127 | N3-PEG6-Alcohol | 86770-69-6 | C12H25N3O6 | 307.3 | |
| 300128 | N3-PEG8-Alcohol | 352439-36-2 | C16H33N3O8 | 395.4 | |
| 300129 | N3-PEG9-Alcohol | N/A | C18H37N3O9 | 439.5 | |
| 300130 | N3-PEG11-Alcohol | N/A | C22H45N3O11 | 527.6 | |
| 300131 | N3-PEG12-alcohol | 73342-16-2 | C24H49N3O12 | 571.7 | |
| 300132 | N3-PEG20-alcohol | 1637297-21-2 | C40H81N3O20 | 924.1 | |
| 300133 | N3-PEG24-alcohol | 73342-16-2 | C48H97N3O24 | 1100.3 | |
| 300134 | N3-PEG36-alcohol | 73342-16-2 | C72H145N3O36 | 1628.9 | |
| 300166 | N3-PEG5-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1415800-41-7 | C17H33N3O7 | 391.46 | |
| 300167 | N3-PEG6-CH2CH2COOtBu | 406213-76-1 | C19H37N3O8 | 435.51 | |
| 300168 | N3-PEG8-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1623791-99-0 | C23H45N3O10 | 523.62 | |
| 300169 | N3-PEG9-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1818294-43-7 | C25H49N3O11 | 567.67 | |
| 300170 | N3-PEG12-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1818294-45-9 | C31H61N3O14 | 699.83 | |
| 300171 | N3-PEG16-CH2CH2COOtBu | N/A | C39H77N3O18 | 876.04 | |
| 300200 | R110-PEG3-Azide | 1536327-95-3 | C29H30N6O7 | 574.59 | |
| 300205 | Methyl-PEG6-Azide | 1043884-49-6 | C13H27N3O6 | 321.37 | |
| 300206 | Methyl-PEG7-Azide | 208987-04-6 | C15H31N3O7 | 365.42 | |
| 300207 | Methyl-PEG8-Azide | 869718-80-9 | C17H35N3O8 | 409.48 | |
| 300208 | Methyl-PEG12-azide | 89485-61-0 | C25H51N3O12 | 585.69 | |
| 300209 | Methyl-PEG24-azide | 89485-61-0 | C49H99N3O24 | 1114.32 | |
| 300210 | Methyl-PEG36-azide | 89485-61-0 | C73H147N3O36 | 1642.95 | |
| 300217 | Boc-N-Amido-PEG4-N3 | 940951-99-5 | C15H30N4O6 | 362.42 | |
| 300218 | Boc-N-amido-PEG5-N3 | 189209-27-6 | C17H34N4O7 | 406.48 | |
| 300224 | 30moc-(azido-PEG4)-L-Lysine | N/A | C32H43N5O9 | 641.71 | |
| 300225 | 30moc-(azido-PEG4)-L-Lysine- P30P | N/A | C38305H42N5O9 | 807.76 | |
| 300232 | Bis-PEG3-CH2CH2COOH | 96517-92-9. | C10H18O7 | 250.25 | |
| 300233 | Bis-PEG4-CH2CH2COOH | 31127-85-2 | C12H22O8 | 294.3 | |
| 300234 | Bis-PEG5-CH2CH2COOH | 439114-13-3 | C14H26O8 | 338.35 | |
| 300235 | Bis-PEG6-CH2CH2COOH | 119189-70-7 | C16H30O10 | 382.4 | |
| 300236 | Bis-PEG7-CH2CH2COOH | 94376-75-7 | C18H34O11 | 426.46 | |
| 300237 | Bis-PEG9-CH2CH2COOH | 1268488-70-5 | C22H42O13 | 514.56 | |
| 300238 | Bis-PEG10-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C24H46O14 | 558.61 | |
| 300239 | Bis-PEG11-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C26H50O15 | 602.67 | |
| 300240 | Bis-PEG13-CH2CH2COOH | 1053656-79-3 | C30H58O17 | 690.77 | |
| 300241 | Bis-PEG14-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C32H62O18 | 734.82 | |
| 300242 | Bis-PEG17-CH2CH2COOH | 51178-68-8 | C38H74O21 | 866.98 | |
| 300243 | Bis-PEG21-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C46H90O25 | 1043.19 | |
| 300244 | Bis-PEG25-CH2CH2COOH | 1268488-70-5 | C54H106O29 | 1219.4 | |
| 300245 | Bis-PEG29-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C62H122O33 | 1395.61 | |
| 300260 | N-Boc-PEG4-alcohol | 106984-09-2 | C13H27NO6 | 293.36 | |
| 300261 | N-Boc-PEG5-alcohol | 1404111-67-6 | C15H31NO7 | 337.41 | |
| 300262 | N-Boc-PEG6-alcohol | 331242-61-6 | C17H35NO8 | 381.46 | |
| 300263 | N-Boc-PEG8-alcohol | 1345337-22-5 | C21H43NO10 | 469.57 | |
| 300264 | N-Boc-PEG12-alcohol | 159156-95-3 | C29H59NO14 | 645.78 | |
| 300265 | N-Boc-PEG16-alcohol | N/A | C37H75NO18 | 821.99 | |
| 300266 | N-Boc-PEG24-alcohol | N/A | C53H107NO26 | 1174.41 | |
| 300267 | N-Boc-PEG36-alcohol | N/A | C77H155NO38 | 1703.04 | |
| 300277 | Boc-N-amido-PEG4-acid | 756525-91-4 | C16H31NO8 | 365.42 | |
| 300278 | Boc-N-amido-PEG5-acid | 1347750-78-0 | C18H35NO9 | 409.47 | |
| 300279 | Boc-N-amido-PEG6-acid | 882847-13-4 | C20H39NO10 | 453.52 | |
| 300280 | Boc-N-amido-PEG7-acid | N/A | C22H43NO11 | 497.58 | |
| 300281 | Boc-N-amido-PEG8-acid | 1334169-93-5 | C24H47NO12 | 541.63 | |
| 300282 | Boc-N-amido-PEG10-acid | N/A | C28H55NO14 | 629.74 | |
| 300283 | Boc-N-amido-PEG12-acid | 187848-68-6 | C32H63NO16 | 717.84 | |
| 300284 | Boc-N-amido-PEG24-acid | 187848-68-6 | C56H111NO28 | 1246.47 | |
| 300285 | Boc-N-amido-PEG36-acid | 187848-68-6 | C80H159NO40 | 1775.1 | |
| 300292 | Boc-N-amido-PEG4-Amine | 811442-84-9 | C15H32N2O6 | 336.42 | |
| 300293 | Boc-N-amido-PEG5-Amine | 189209-27-6 | C17H36N2O7 | 380.48 | |
| 300294 | Boc-N-amido-PEG6-Amine | 1091627-77-8 | C19H40N2O8 | 424.53 | |
| 300295 | Boc-N-amido-PEG7-Amine | 206265-98-7 | C21H44N2O9 | 468.58 | |
| 300296 | Boc-N-amido-PEG9-Amine | 890091-43-7 | C25H52N2O11 | 556.69 | |
| 300297 | Boc-N-amido-PEG11-Amine | 198227-38-2 | C29H60N2O13 | 644.79 | |
| 300298 | Boc-N-amido-PEG15-Amine | 198227-38-2 | C37H76N2O17 | 821 | |
| 300299 | Boc-N-amido-PEG23-Amine | 198227-38-2 | C53H108N2O25 | 1173.42 | |
| 300300 | Boc-N-amido-PEG5-NHS | N/A | C22H38N2O11 | 506.54 | |
| 300307 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG4-acid | 557756-85-1 | C26H33NO8 | 487.54 | |
| 300308 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG5-acid | 882847-32-7 | C28H37NO9 | 531.6 | |
| 300309 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG6-acid | 882847-34-9 | C30H41NO10 | 575.65 | |
| 300310 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG7-acid | N/A | C32H45NO11 | 619.7 | |
| 300311 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG8-acid | 756526-02-0 | C34H49NO12 | 663.75 | |
| 300312 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG9-acid | 1191064-81-9 | C36H53NO13 | 707.81 | |
| 300313 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG10-Acid | N/A | C38H57NO14 | 751.86 | |
| 300314 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG12-Acid | 756526-01-9 | C42H65NO16 | 839.96 | |
| 300315 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG20-acid | 1952360-93-8 | C58H97NO24 | 1192.38 | |
| 300316 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG24-acid | 756526-01-9 | C66H113NO28 | 1368.59 | |
| 300317 | 30moc-N-amido-PEG36-acid | N/A | C90H161NO40 | 1897.22 | |
| 300328 | 30moc-NH-PEG4-NHS | 1314378-14-7 | C30H36N2O10 | 584.61 | |
| 300329 | 30moc-NH-PEG5-NHS | 1402080-11-8 | C32H40N2O11 | 628.67 | |
| 300330 | 30moc-NH-PEG6-NHS | 1818294-31-3 | C34H44N2O12 | 672.72 | |
| 300331 | 30moc-NH-PEG8-NHS | 1334170-03-4 | C38H52N2O14 | 760.83 | |
| 300332 | 30moc-NH-PEG12-NHS | N/A | C46H68N2O18 | 937.03 | |
| 300442 | Hydroxy-PEG6-CH2CH2COOH | 1347750-85-9 | C15H30O9 | 354.39 | |
| 300443 | Hydroxy-PEG8-CH2CH2COOH | 937188-60-8 | C19H38O11 | 442.5 | |
| 300444 | Hydroxy-PEG12-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C27H54O15 | 618.71 | |
| 300445 | Hydroxy-PEG14-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C31H62O17 | 706.8 | |
| 300446 | Hydroxy-PEG16-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C35H70O19 | 794.92 | |
| 300467 | Hydroxy-PEG6-CH2CH2COOtBu | 361189-64-2 | C19H38O9 | 410.5 | |
| 300468 | Hydroxy-PEG8-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1334177-84-2 | C23H46O11 | 498.61 | |
| 300469 | Hydroxy-PEG9-CH2CH2COOtBu | N/A | C25H50O12 | 542.66 | |
| 300470 | Hydroxy-PEG10-CH2CH2COOtBu | 778596-26-2 | C27H54O13 | 586.71 | |
| 300471 | Hydroxy-PEG12-CH2CH2COOtBu | 892154-71-1 | C31H62O15 | 674.82 | |
| 300472 | Hydroxy-PEG13-CH2CH2COOtBu | N/A | C33H66O16 | 718.87 | |
| 300473 | Hydroxy-PEG14-CH2CH2COOtBu | N/A | C35H70O17 | 762.92 | |
| 300474 | Hydroxy-PEG16-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1186025-29-5 | C39H78O19 | 851.03 | |
| 300475 | Hydroxy-PEG20-CH2CH2COOtBu | N/A | C47H94O23 | 1027.23 | |
| 300476 | Hydroxy-PEG24-CH2CH2COOtBu | 1186025-29-5 | C55H110O27 | 1203.45 | |
| 300487 | Amino-PEG6-alcohol | 39160-70-8 | C12H27NO6 | 281.35 | |
| 300488 | Amino-PEG7-alcohol | 1425973-14-3 | C14H31NO7 | 325.4 | |
| 300489 | Amino-PEG8-alcohol | 352439-37-3 | C16H35NO8 | 369.45 | |
| 300490 | Amino-PEG10-alcohol | 129449-09-8 | C20H43NO10 | 457.56 | |
| 300491 | Amino-PEG12-alcohol | 933789-97-0 | C24H51NO12 | 545.66 | |
| 300492 | Amino-PEG24-alcohol | 933789-97-0 | C48H99NO24 | 1074.29 | |
| 300493 | Amino-PEG36-alcohol | 933789-97-0 | C72H147NO36 | 1602.92 | |
| 300503 | Methyl-PEG8-alcohol | 25990-96-9 | C17H36O9 | 384.46 | |
| 300504 | Methyl-PEG9-alcohol | 6048-68-6 | C19H40O10 | 428.52 | |
| 300505 | Methyl-PEG10-alcohol | 27425-92-9 | C21H44O11 | 472.57 | |
| 300506 | Methyl-PEG11-alcohol | 114740-40-8 | C23H48O12 | 516.62 | |
| 300507 | Methyl-PEG12-alcohol | 5702-16-9 | C25H52O13 | 560.67 | |
| 300508 | Methyl-PEG15-alcohol | 9004-74-4 | C31H64O16 | 692.83 | |
| 300509 | Methyl-PEG16-alcohol | 133604-58-7 | C33H68O17 | 736.88 | |
| 300510 | Methyl-PEG19-alcohol | N/A | C39H80O20 | 869.04 | |
| 300511 | Methyl-PEG23-alcohol | N/A | C47H96O24 | 1045.25 | |
| 300512 | Methyl-PEG24-alcohol | 114740-40-8 | C49H100O25 | 1089.3 | |
| 300513 | Methyl-PEG36-alcohol | 114740-40-8 | C73H148O37 | 1617.93 | |
| 300514 | Methyl-PEG48-alcohol | 114740-40-8 | C97H196O49 | 2146.56 | |
| 300520 | PropargylPEG6-alcohol | 1036204-60-0 | C13H24O6 | 276.33 | |
| 300521 | PropargylPEG7-alcohol | 944560-99-0 | C15H28O7 | 320.38 | |
| 300522 | PropargylPEG8-alcohol | 1422023-54-8 | C17H32O8 | 364.43 | |
| 300523 | PropargylPEG9-alcohol | 1351556-81-4 | C19H36O9 | 408.48 | |
| 300524 | PropargylPEG10-alcohol | N/A | C21H40O10 | 452.54 | |
| 300525 | PropargylPEG13-alcohol | 1036204-61-1 | C27H52O13 | 584.69 | |
| 300526 | PropargylPEG14-alcohol | N/A | C29H56O14 | 628.75 | |
| 300527 | PropargylPEG18-alcohol | N/A | C37H72O18 | 804.96 | |
| 300544 | PEG11 | 5579-66-8 | C20H42O11 | 458.54 | |
| 300545 | PEG12 | 6809-70-7 | C22H46O12 | 502.59 | |
| 300546 | PEG13 | 6790-0 9-6 | C24H50O13 | 546.65 | |
| 300547 | PEG15 | 1189112-05-7 | C28H58O15 | 634.75 | |
| 300548 | PEG16 | 28821-35-4 | C30H62O16 | 678.8 | |
| 300549 | PEG17 | 4669-05-0 | C32H66O17 | 722.86 | |
| 300550 | PEG18 | 351342-04-6 | C34H70O18 | 766.91 | |
| 300551 | PEG22 | 928211-42-1 | C42H86O22 | 943.12 | |
| 300552 | PEG24 | N/A | C48H98O25 | 1075.28 | |
| 300562 | Methyl-PEG6-acid | 1347750-72-4 | C14H28O8 | 324.37 | |
| 300563 | Methyl-PEG7-acid | 874208-91-0 | C16H32O9 | 368.42 | |
| 300564 | Methyl-PEG8-CH2CH2COOH | 1093647-41-6 | C18H36O10 | 412.47 | |
| 300565 | Methyl-PEG9-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C20H40O11 | 456.53 | |
| 300566 | Methyl-PEG10-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C22H44O12 | 500.58 | |
| 300567 | Methyl-PEG11-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C24H48O13 | 544.63 | |
| 300568 | Methyl-PEG12-CH2CH2COOH | 125220-94-2 | C26H52O14 | 588.68 | |
| 300569 | Methyl-PEG13-CH2CH2COOH | 1239588-11-4 | C28H56O15 | 632.74 | |
| 300570 | Methyl-PEG16-CH2CH2COOH | 125220-94-2 | C34H68O18 | 764.89 | |
| 300571 | Methyl-PEG17-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C36H72O19 | 808.95 | |
| 300572 | Methyl-PEG24-CH2CH2COOH | 125220-94-2 | C50H100O26 | 1117.31 | |
| 300573 | Methyl-PEG25-CH2CH2COOH | 125220-94-2 | C52H104O27 | 1161.37 | |
| 300574 | Methyl-PEG37-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C52H104O27 | 1690 | |
| 300575 | Methyl-PEG49-CH2CH2COOH | 125220-94-2 | C100H200O51 | 2218.63 | |
| 300591 | Methyl-PEG8-amine | 869718-81-0 | C17H37NO8 | 383.48 | |
| 300592 | Methyl-PEG9-amine | 211859-73-3 | C19H41NO9 | 427.53 | |
| 300593 | Methyl-PEG10-amine | 1383658-09-0 | C21H45NO10 | 471.58 | |
| 300594 | Methyl-PEG11-amine | 854601-60-8 | C23H49NO11 | 515.64 | |
| 300595 | Methyl-PEG12-amine | 869718-87-6 | C25H53NO12 | 559.69 | |
| 300596 | Methyl-PEG15-amine | N/A | C31H65NO15 | 691.85 | |
| 300597 | Methyl-PEG24-amine | 32130-27-1 | C49H101NO24 | 1088.32 | |
| 300598 | Methyl-PEG36-amine | 32130-27-1 | C73H149NO36 | 1616.95 | |
| 300599 | Methyl-PEG48-amine | 32130-27-1 | C97H197NO48 | 2145.58 | |
| 300617 | Methyl-PEG8-Mal | 1334169-90-2 | C24H42N2O11 | 534.6 | |
| 300618 | Methyl-PEG12-Mal | 88504-24-9 | C32H58N2O15 | 710.81 | |
| 300619 | Methyl-PEG24-Mal | 88504-24-9 | C56H106N2O27 | 1239.44 | |
| 300620 | Methyl-PEG36-Mal | 88504-24-9 | C80H154N2O39 | 1768.07 | |
| 300621 | Methyl-PEG48-Mal | 88504-24-9 | C104H202N2O51 | 2296.7 | |
| 300631 | Methyl-PEG8-NHS | 756525-90-3 | C22H39NO12 | 509.55 | |
| 300632 | Methyl-PEG9-NHS | 1316189-13-5 | C24H43NO13 | 553.6 | |
| 300633 | Methyl-PEG11-NHS | N/A | C28H51NO15 | 641.7 | |
| 300634 | Methyl-PEG12-NHS | 174569-25-6 | C30H55NO16 | 685.76 | |
| 300635 | Methyl-PEG13-NHS | 174569-25-6 | C32H59NO17 | 729.81 | |
| 300636 | Methyl-PEG24-NHS | 174569-25-6 | C54H103NO28 | 1214.39 | |
| 300648 | Methyl-PEG7-tBu ester | 874208-90-9 | C20H40O9 | 424.53 | |
| 300649 | Methyl-PEG12-tBu ester | N/A | C30H60O14 | 644.79 | |
| 300669 | Mal-PEG4-CH2CH2COOH | 518044-41-2 | C15H23NO8 | 345.35 | |
| 300670 | Mal-PEG5-acid | 1286755-26-7 | C17H27NO9 | 389.4 | |
| 300671 | Mal-PEG6-CH2CH2COOH | 518044-42-3 | C19H31NO10 | 433.45 | |
| 300672 | Mal-PEG8-CH2CH2COOH | 1818294-46-0 | C23H39NO12 | 521.56 | |
| 300681 | Mal-PEG4-NHS | 1325208-25-0 | C19H26N2O10 | 442.42 | |
| 300684 | Mal-PEG8-NHS | N/A | C27H42N2O14 | 618.63 | |
| 300688 | Mal-PEG4-P30P | 1415800-42-8 | C21305H22NO8 | 511.39 | |
| 300690 | Mal-PEG6-P30P | 1599486-33-5 | C25305H30NO10 | 599.5 | |
| 300699 | Mal-Amido-PEG4-acid | 1263045-16-4 | C18H28N2O9 | 416.42 | |
| 300700 | Mal-amido-PEG6-acid | 1334177-79-5 | C22H36N2O11 | 504.53 | |
| 300701 | Mal-amido-PEG8-acid | 1334177-86-4 | C26H44N2O13 | 592.63 | |
| 300702 | Mal-amido-PEG10-acid | N/A | C30H52N2O15 | 680.74 | |
| 300703 | Mal-amido-PEG12-acid | 871133-36-7 | C34H60N2O17 | 768.84 | |
| 300704 | Mal-N-amido-PEG24-CH2CH2COOH | 871133-36-7 | C58H108N2O29 | 1297.47 | |
| 300706 | Mal-amido-PEG4-NHS | 756525-99-2 | C22H31N3O11 | 513.5 | |
| 300707 | Mal-amido-PEG6-NHS | 1137109-21-7 | C26H39N3O13 | 601.6 | |
| 300708 | Mal-amido-PEG8-NHS | 756525-93-6 | C30H47N3O15 | 689.71 | |
| 300709 | Mal-amido-PEG12-NHS | 756525-92-5 | C38H63N3O19 | 865.92 | |
| 300710 | Mal-amido-PEG24-NHS | 326003-46-7 | C62H111N3O31 | 1394.55 | |
| 300727 | Bis-Mal-PEG6 | N/A | C28H42N4O12 | 626.65 | |
| 300728 | Bis-Mal-PEG11 | N/A | C38H62N4O17 | 846.92 | |
| 300729 | Bis-Mal-PEG19 | N/A | C54H94N4O25 | 1199.34 | |
| 300741 | Amino-PEG6-CH2CH2COOH | 905954-28-1 | C15H31NO8 | 353.41 | |
| 300742 | Amino-PEG8-CH2CH2COOH | 756526-04-2 | C19H39NO10 | 441.51 | |
| 300743 | Amino-PEG9-CH2CH2COOH | 1191079-83-0 | C21H42NO11 | 484.56 | |
| 300744 | Amino-PEG10-CH2CH2COOH | 1818294-41-5 | C23H47NO12 | 529.62 | |
| 300745 | Amino-PEG12-CH2CH2COOH | 1186194-33-1 | C27H55NO14 | 617.72 | |
| 300747 | Amino-PEG16-CH2CH2COOH | 196936-04-6 | C35H71NO18 | 793.93 | |
| 300748 | Amino-PEG20-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C43H87NO22 | 970.14 | |
| 300749 | Amino-PEG23-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C49H99NO25 | 1102.3 | |
| 300750 | Amino-PEG24-CH2CH2COOH | 756526-07-4 | C51H103NO26 | 1146.35 | |
| 300751 | Amino-PEG25-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C53H107NO27 | 1190.41 | |
| 300752 | Amino-PEG28-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C59H119NO30 | 1322.56 | |
| 300753 | Amino-PEG32-CH2CH2COOH | N/A | C67H135NO34 | 1498.78 | |
| 300754 | Amino-PEG36-CH2CH2COOH | 756526-07-4 | C75H151NO38 | 1674.98 | |
| 300769 | Azido-PEG8-acid | 1214319-92-2 | C19H37N3O10 | 467.51 | |
| 300770 | Azido-PEG9-acid | 1670249-37-2 | C21H41N3O11 | 511.56 | |
| 300771 | Azido-PEG10-acid | 1644163-57-4 | C23H45N3O12 | 555.62 | |
| 300772 | Azido-PEG12-acid | 1167575-20-3 | C27H53N3O14 | 643.72 | |
| 300773 | Azido-PEG24-acid | 1167575-20-3 | C51H101N3O26 | 1172.35 | |
| 300779 | Cbz-N-amido-PEG4-acid | 756526-00-8 | C19H29NO8 | 399.44 | |
| 300780 | Cbz-N-amido-PEG5-acid | 1347750-74-6 | C21H33NO9 | 443.49 | |
| 300781 | Cbz-N-amido-PEG6-acid | 1334177-80-8 | C23H37NO10 | 487.54 | |
| 300782 | Cbz-N-amido-PEG8-acid | 1334177-87-5 | C27H45NO12 | 575.65 | |
| 300783 | Cbz-N-amido-PEG10-acid | N/A | C31H53NO14 | 663.75 | |
| 300787 | Biotin-PEG4-Acid | 721431-18-1 | C21H37N3O8S | 491.6 | |
| 300788 | Biotin-PEG6-Acid | 1352814-10-8 | C25H45N3O10S | 579.71 | |
| 300789 | Biotin-PEG8-acid | N/A | C29H53N3O12S | 667.81 | |
| 300790 | Biotin-PEG12-Acid | 1621423-14-0 | C37H69N3O16S | 844.02 | |
| 300791 | Biotin-PEG24-Acid | 721431-18-1 | C61H117N3O28S | 1372.65 | |
| 300808 | HOOCCH2CH2-PEG4-NHS | 1343476-41-4 | C18H29NO11 | 435.42 | |
| 300809 | HOOCCH2CH2-PEG8-NHS | 1895916-27-4 | C26H45NO15 | 611.63 | |
| 300810 | HOOCCH2CH2-PEG12-NHS | N/A | C34H61NO19 | 787.84 | |
| 300811 | HOOCCH2CH2-PEG24-NHS | N/A | C58H109NO31 | 1316.47 | |
| 300819 | Azido-PEG6-NHS | N/A | C19H32N4O10 | 476.48 | |
| 300820 | Azido-PEG8-NHS | 1204834-00-3 | C23H40N4O12 | 564.58 | |
| 300821 | Azido-PEG12-NHS | 1610796-02-5 | C31H56N4O16 | 740.79 | |
| 300943 | Thiol-PEG8-acid | 866889-02-3 | C19H38O10S | 458.57 | |
| 300944 | Thiol-PEG12-acid | 1032347-93-5 | C27H54O14S | 634.78 | |
| 300973 | S-acetyl-PEG6-alcohol | 1352221-63-6 | C14H28O7S | 340.43 | |
| 300974 | S-acetyl-PEG8 alcohol | 1334177-81-9 | C18H36O9S | 428.54 | |
| 300975 | S-acetyl-PEG12 alcohol | N/A | C26H52O13S | 604.75 | |
| 300976 | S-acetyl-PEG16 alcohol | N/A | C34H68O17S | 780.96 | |
| 300977 | S-acetyl-PEG20 alcohol | N/A | C42H84O21S | 957.17 | |
| 300986 | SPDP-PEG8-acid | 1334177-96-6 | C27H46N2O11S2 | 638.79 | |
| 300987 | SPDP-PEG12-acid | N/A | C35H62N2O15S2 | 815 | |
| 300988 | SPDP-PEG24-acid | N/A | C59H110N2O27S2 | 1343.63 | |
| 300989 | SPDP-PEG36-acid | N/A | C83H158N2O39S2 | 1872.27 | |
| 300990 | SPDP-PEG4-NHS | 1334177-95-5 | C23H33N3O9S2 | 559.66 | |
| 300991 | SPDP-PEG6-NHS | 1818294-32-4 | C27H41N3O11S2 | 647.76 | |
| 300992 | SPDP-PEG8-NHS | 1252257-56-9 | C31H49N3O13S2 | 735.87 | |
| 300993 | SPDP-PEG12-NHS | N/A | C39H65N3O17S2 | 912.08 | |
| 300994 | SPDP-PEG-24-NHS | N/A | C64H114N2O29S2 | 1439.72 | |
| 300995 | SPDP-PEG36-NHS | N/A | C88H162N2O41S2 | 1968.35 | |
| 300996 | SPDP-PEG6-tBu ester | 1818294-34-6 | C27H46N2O9S2 | 606.79 | |
| 300997 | Boc-Ser(Azido-PEG3)-OH | 1101193-38-7 | C14H26N4O7 | 362.38 | |
| 300998 | Boc-Ser(mPEG2)-OH | 150438-69-0 | C13H25NO7 | 307.34 | |
| 300999 | N-Boc-O-(2-benzyloxyethyl)-L-serine | N/A | C17H25NO6 | 339.39 | |
| 301000 | N-CBz-O-(2-benzyloxyethyl)-L-serine | 159526-79-1 | C20H23NO6 | 373.41 | |
| 301001 | Cbz-Ser(azido-PEG2)-OH | 159526-82-6 | C15H20N4O6 | 352.35 | |
| 301002 | (+)-(2S)-9-benzyloxy-2-(N-benzyloxycarbonylamino)- 4,7-dioxanonanoic acid |
159526-80-4 | C22H27NO7 | 417.46 | |
| 301003 | (+)-(2S)-12-azido-2-(N-benzyloxycarbonylamino)- 4,7,10-trioxadodecanoic acid |
159526-83-7 | C17H24N4O7 | 396.4 | |
| 301004 | (+)-(2S)-12-benzyloxy-2-(N-benzyloxycarbonylamino)- 4,7,10-trioxadodecanoic acid |
159526-81-5 | C24H31NO8 | 461.51 | |
| 301005 | Boc-Ser(MPEG1)-OH | N/A | C11H21NO6 | 263.29 | |
| 301006 | N-benzyloxycarbonyl-3-{2-[2-(2-methoxyethoxy) ethoxy]ethyl}-L-serine |
919297-27-1 | C18H27NO8 | 385.41 | |
| 301007 | 30moc-Ser(azido-PEG3)-OH | 1101193-41-2 | C24H28N4O7 | 484.51 | |
| 301008 | Boc-Ser(azido-PEG2)-OH | N/A | C12H22N4O6 | 318.33 | |
| 301009 | Boc-Ser(azido-PEG4)-OH | N/A | C16H30N4O8 | 406.44 | |
| 301010 | 30moc-Tyr(azido-PEG3)-OH | 1263721-25-0 | C30H32N4O7 | 560.61 | |
| 301011 | Boc-Tyr(PEG3)-OH | N/A | C20H31NO8 | 413.47 | |
| 301012 | Boc-Tyr(azido-PEG3)-OH | N/A | C20H30N4O7 | 438.48 | |
| 301013 | 30moc-Lys(azido-Peg5)-OH | N/A | C34H47N5O10 | 685.78 | |
| 301014 | Nα-30moc-lysine(mPEG24)-OH | N/A | C71H122N2O29 | 1467.75 | |
| 301015 | N2-30luorenylmethoxycarbonyl-N4-{14-tertBuoxycarbonyl- 3,6,9,12-tetraoxatetradecyl}-L-asparagine |
930806-24-9 | C34H46N2O11 | 658.75 | |
| 301016 | Biotin-PEG2-NHS | 596820-83-6 | C21H32N4O8S | 500.57 | |
| 301017 | Biotin-PEG3-NHS | 1253286-56-4 | C23H36N4O9S | 544.62 | |
| 301018 | Biotin-PEG4-NHS | 459426-22-3 | C25H40N4O10S | 588.67 | |
| 301019 | Biotin-PEG6-NHS | N/A | C29H48N4O12S | 676.78 | |
| 301020 | Biotin-PEG8-NHS | N/A | C33H56N4O14S | 764.88 | |
| 301021 | Biotin-PEG12-NHS | 365441-71-0 | C41H72N4O18S | 941.09 | |
| 301022 | Biotin-PEG24-NHS | N/A | C65H120N4O30S | 1469.73 |
Not for direct human use.
Resource
PEGylation is the process of both covalent and non-covalent attachment or amalgamation of polyethylene glycol (PEG, in pharmacy called macrogol) polymer chains to molecules and macrostructures, such as a drug, therapeutic protein or vesicle, which is then described as PEGylated. PEGylation is routinely achieved by the incubation of a reactive derivative of PEG with the target molecule. The covalent attachment of PEG to a drug or therapeutic protein can "mask" the agent from the host's immune system (reducing immunogenicity and antigenicity), and increase its hydrodynamic size (size in solution), which prolongs its circulatory time by reducing renal clearance. PEGylation can also provide water solubility to hydrophobic drugs and proteins. Having proven its pharmacological advantages and acceptability, PEGylation technology is the foundation of a growing multibillion-dollar industry.
PEGylated pharmaceuticals on the market
The attachment of an inert and hydrophilic polymer was first reported around 1970 to extend blood life and control immunogenicity of proteins. Polyethylene glycol was chosen as the polymer. In 1981 Davis and Abuchowski founded Enzon, Inc., which brought three PEGylated drugs to market. Abuchowski later founded and is CEO of Prolong Pharmaceuticals.
The clinical value of PEGylation is now well established. ADAGEN (pegademase bovine) manufactured by Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc., US was the first PEGylated protein approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 1990, to enter the market. It is used to treat a form of severe combined immunogenicity syndrome (ADA-SCID), as an alternative to bone marrow transplantation and enzyme replacement by gene therapy. Since the introduction of ADAGEN, a large number of PEGylated protein and peptide pharmaceuticals have followed and many others are under clinical trial or under development stages. Sales of the two most successful products, Pegasys and Neulasta, exceeded $5 billion in 2011. All commercially available PEGylated pharmaceuticals contain methoxypoly(ethylene glycol) or mPEG. PEGylated pharmaceuticals on the market (in reverse chronology by FDA approval year) have included:
- Pegvaliase (Biomarin) – PEGylated recombinant phenylalanine ammonia-lyase for the treatment of Phenylketonuria, approved by the FDA for the US in May 2018.
- Adynovate – PEGylated Antihemophilic Factor VIII for the treatment of patients with hemophilia A. (Baxalta, 2015)
- Plegridy – PEGylated Interferon Beta-1a for the treatment of patients with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis. (Biogen, 2014)
- Naloxegol (Movantik) – PEGylated naloxol for the treatment of opioid-induced constipation in adults patients with chronic non-cancer pain (un-pegylated methadone can cause adverse gastrointestinal reactions). (AstraZeneca, 2014)
- Peginesatide (Omontys) – once-monthly medication to treat anemia associated with chronic kidney disease in adult patients on dialysis (Affymax/Takeda Pharmaceuticals, 2012)
- Pegloticase (Krystexxa) – PEGylated uricase for the treatment of gout (Savient, 2010)
- Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) – monoclonal antibody for treatment of moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease, an inflammatory gastrointestinal disorder (Nektar/UCB Pharma, 2008)
- Methoxy polyethylene glycol-epoetin beta (Mircera) – PEGylated form of erythropoietin to combat anemia associated with chronic kidney disease (Roche, 2007)
- Pegaptanib (Macugen) – used to treat neovascular age-related macular degeneration (Pfizer, 2004)
- Pegfilgrastim (Neulasta) – PEGylated recombinant methionyl human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for severe cancer chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (Amgen, 2002)
- Pegvisomant (Somavert) – PEG-human growth hormone mutein antagonist for treatment of Acromegaly (Pfizer, 2002)
- Peginterferon alfa-2a (Pegasys) – PEGylated interferon alpha for use in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C and hepatitis B (Hoffmann-La Roche, 2002)
- Peginterferon alfa-2b (PegIntron) – PEGylated interferon alpha for use in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C and hepatitis B (Schering-Plough/Enzon, 2000)
- Doxorubicin HCl liposome (Doxil/Caelyx) – PEGylated liposome containing doxorubicin for the treatment of cancer (Alza, 1995)
- Pegaspargase (Oncaspar) – PEGylated L-asparaginase for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in patients who are hypersensitive to the native unmodified form of L-asparaginase (Enzon, 1994). This drug was recently approved for front line use.
- Pegademase bovine (Adagen) – PEG-adenosine deaminase for the treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) (Enzon, 1990)
Recommended reading
- Hermanson, G.T. (2013). 3rd Edition. Bioconjugate Techniques, Academic Press.
- Harris, J. M. and Zalipsky, S. Eds (1997). Poly(ethylene glycol), Chemistry and Biological Applications, ACS Symposium Series, 680.
- Harris, J. M. and Kozlowski, A. (2001). Improvements in protein PEGylation: pegylated interferons for treatment of hepatitis C. J. Control Release 72, 217-224.
- Veronese, F. and Harris, J.M. Eds. (2002). Peptide and protein PEGylation. Advanced Drug Delivery Review 54(4), 453-609.
- Prime, K.L. and Whitesides, G.M. (1991). Self-assembled organic monolayers: model systems for studying absorption of proteins at surfaces. Science 252:1164.
- Bentzen, E.L., et al. (2005). Surface modification to reduce non-specific binding of quantum dots in live cell assays. Bioconjugate Chem 16:1488-94.
- Lin, P-C., et al. (2006). Ethylene glycol-protected magnetic nanoparticles for a multiplexed immunoassay in human plasma. Small 2(4):485-9.
- Zheng, M., et al. (2003). Ethylene glycol monolayer protected nanoparticles for eliminating nonspecific binding with biological molecules. J Am Chem Soc 125:7790-1.
- Verma, A. and Rotello, V.M. (2005). Surface recognition of biomacromolecules using nanoparticle receptors. Chem Commun 3:303-12.
- Kidambi, S., et al. (2004). Selective depositions on polyelectrolyte multilayers: self-assembled monolayers of m-dPEG acid as molecular template. J Am Chem Soc 126:4697-4703.
1-1.png)
